| Fix thermal properties
|
When on, all calculated thermal properties in the
Construction Details panel are overridden, enabling you to define your own
thermal properties. When off, the calculated thermal properties are used.
|
| Total Thickness
|
Displays the selected construction’s total
thickness which includes all the material layers that make up the construction.
|
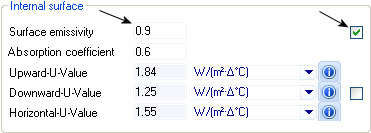
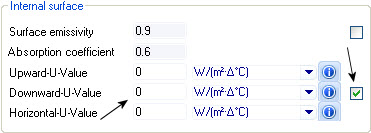
| Internal surface
|
Displays thermal transfer properties for the inside
surface of the selected construction.
- Surface emissivity
— Displays the selected construction's internal surface emissivity factor.
Surface emissivity is a measure of the efficiency in which a surface emits
thermal energy. It is defined as the fraction of energy being emitted relative
to that emitted by a thermally black surface (a black body). A black body is a
material that is a perfect emitter of heat energy and has an emissivity value
of 1. A material with an emissivity value of 0 would be considered a perfect
thermal mirror.
- Absorption
coefficient — Displays the absorption coefficient for the selected
construction's internal surface. The absorption coefficient is a number between
0 and 1. The lower a construction's inside surface solar absorption
coefficient, the less solar heat it transmits.
- Fix thermal
properties check box (Surface emissivity, Absorption coefficient) — When on,
calculated surface emissivity and absorption coefficient are overridden,
enabling you to define your own thermal properties. The background color on the
value fields is changed to white indicating the field is read writable, When
off, the calculated transmission properties are used. All value fields are
read-only.
- Upward-U-Value —
Displays the calculated inside surface U-value or thermal transmittance of
energy traveling upward through the selected construction.
- Downward-U-Value —
Displays the calculated inside surface U-value or thermal transmittance of
energy traveling downward through the selected construction.
- Horizontal-U-Value
— Displays the calculated inside surface U-value or thermal transmittance of
energy traveling horizontally through the selected construction.
- Fix thermal
properties check box (Upward-U-Value, Downward-U-Value, Horizontal-U-Value) —
When on, all upward, downward, and horizontal U-values calculated thermal
properties are overridden, enabling you to define your own thermal properties.
The background color on the value fields is changed to white indicating the
field is read writable, When off, the calculated U-values are used. All value
fields are read-only.
- Decrement factor —
Displays a decrement factor which is the decreasing amplitude of the thermal
wave during its propagation process from outside through the construction
inside surface.
- Admittance —
Displays the amount of heat that passes through a unit area of the construction
inside surface, when its opposite faces are subject to a unit temperature
change.
- Time lag — Displays
the time taken for heat generated by the sun to transfer from the outside,
through the construction inside surface, and affect the internal conditions.
- Weight — Displays
the construction inside surface weight per unit area.
Tip:
You can open the
Results Viewer utility to step
through the calculations of the selected construction’s U-Value properties by
selecting the information icons next to the values.
|
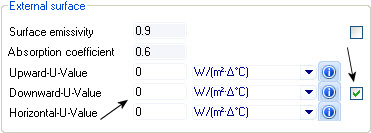
| External surface
|
Displays thermal transfer properties for the
external surface of the selected construction.
- Surface emissivity
— Displays the selected construction's external surface emissivity factor.
Surface emissivity is a measure of the efficiency in which a surface emits
thermal energy. It is defined as the fraction of energy being emitted relative
to that emitted by a thermally black surface (a black body). A black body is a
material that is a perfect emitter of heat energy and has an emissivity value
of 1. A material with an emissivity value of 0 would be considered a perfect
thermal mirror.
- Absorption
coefficient — Displays the absorption coefficient for the selected
construction's external surface. The absorption coefficient is a number between
0 and 1. The lower a construction's external surface solar absorption
coefficient, the less solar heat it transmits.
- Fix thermal
properties check box (Surface emissivity, Absorption coefficient) — When on,
calculated surface emissivity and absorption coefficient are overridden,
enabling you to define your own thermal properties. The background color on the
value fields is changed to white indicating the field is read writable,When
off, the calculated transmission properties are used. All value fields are
read-only.
- Upward-U-Value —
Displays the calculated outside surface U-value or thermal transmittance of
energy traveling upward through the selected construction.
- Downward-U-Value —
Displays the calculated outside surface U-value or thermal transmittance of
energy traveling downward through the selected construction.
- Horizontal-U-Value
— Displays the calculated outside surface U-value or thermal transmittance of
energy traveling horizontally through the selected construction.
- Fix thermal
properties check box (Upward-U-Value, Downward-U-Value, Horizontal-U-Value) —
When on, all upward, downward, and horizontal U-values calculated thermal
properties are overridden, enabling you to define your own thermal properties.
The background color on the value fields is changed to white indicating the
field is read writable,When off, the calculated U-values are used. All value
fields are read-only.
- Decrement factor —
Displays a decrement factor which is the decreasing amplitude of the thermal
wave during its propagation process from outside through the construction
outside surface.
- Admittance —
Displays the amount of heat that passes through a unit area of the construction
outside surface, when its opposite faces are subject to a unit temperature
change.
- Time lag — Displays
the time taken for heat generated by the sun to transfer from the outside,
through the construction outside surface, and affect the internal conditions.
- Weight — Displays
the construction outside surface weight per unit area.
Tip: You can open the
Results Viewer utility to step
through the calculations of the selected construction’s U-Value properties by
selecting the information icons next to the values.
|
| Ground floor
|
Contains controls for defining ground floor data in
addition to the fabric materials that make up the floor construction. The sum
of the ground floor properties and fabric data is considered in determining the
thermal properties of the ground floor.
- Underfloor space
height — For ground floors with an outside air space below. Displays the height
above the solid ground to the underside of the exposed floor.
- Ventilation opening
area — Displays the total area of ventilation openings in the selected
construction.
- Insulation type —
Displays the insulation type to consider for the ground floor.
- Insulation material
— Used to display and select the insulation material to be considered for the
ground floor. Select from the available materials in the drop-down list
provided.
- Insulation
thickness — Displays the insulation thickness to be considered for the ground
floor.
- Insulation width —
Displays the total insulation width to be considered for the ground floor.
|
| Below-grade walls/floors
|
Contains options for entering overriding C-factors
and F-factors for below-grade walls and floors whose construction is not
adequately represented by the assumptions in the ASHRAE 90.1 standard’s
Normative Appendix A (rated R-Value of insulation and assembly U-Factor,
C-Factor, and F-Factor determinations).
The settings under the Below-grade walls/floors
heading are enabled when the Fix thermal properties options are checked.
- Below-grade wall
with an overriding C-factor — When on, enables the Overriding C-factor value
field.
- Slab-on-grade floor
with an overriding F-factor — When on, enables the Overriding F-factor value
field.
- Overriding C-factor
— Used to enter an overriding C-factor for below grade walls.
- Overriding F-factor
— Used to enter an overriding F-factor for slab on grade floors.
|
| Glazing (windows only)
|
Contains controls for defining glazing data in
addition to the fabric materials that make up the window construction. The sum
of the window properties and fabric data is considered in determining the
thermal properties of the window.
- Glazed amount —
Displays the amount of glazing the window has as a percentage or as a ratio.
- Light transmittance
— Displays the amount of daylight striking the window glazing that passes
through to the inside as a ratio. Glazings with a high light transmittance
appear relatively clear and provide sufficient daylight and unaltered views;
however, they can create glare problems. Glazings with low light transmittance
are best used in highly glare-sensitive conditions, but can create gloomy
interiors under some weather conditions and diminished views.
- Average solar gain
factor air — Used to calculate total heat gain through the window, the Average
solar gain factor air property represents the average solar gain over a 24 hour
period for the air space between the inside surface of the window glass and
internal shading. Solar gain factor refers to an estimate of the heat gain due
to transmitted and absorbed solar energy through a benchmark glazing (1/8 or 3
mm clear glass) at a specific latitude, time and orientation.
- Cyclic solar gain
factor air — Used to calculate total heat gain through the window, the Cyclic
solar gain factor air property represents the hourly swing of the solar gain
over a 24 hour period for the air space between the inside surface of the
window glass and internal shading. Solar gain factor refers to an estimate of
the heat gain due to transmitted and absorbed solar energy through a benchmark
glazing (1/8 or 3 mm clear glass) at a specific latitude, time and
orientation.
- Shading coefficient
— Displays the Shading coefficient value associated with the window. This
dimensionless indicator is the ratio of the solar heat gain of the selected
glazing compared to a benchmark glazing (1/8 or 3 mm clear glass) under
identical conditions. The Shading coefficient along with the Solar heat gain
coefficient indicate the total solar heat gain and are used in cooling load
calculations.
- Solar heat gain
coefficient — Displays the Solar heat gain coefficient value associated with
the window. This dimensionless indicator is the ratio of the total transmitted
solar heat energy to incident solar energy. It typically ranges from 0.9 to 0.1
where lower values indicate lower solar gain. The Solar heat gain coefficient
along with the Shading coefficient indicate the total solar heat gain and are
used in cooling load calculations.
- Average solar gain
factor env. — Used to calculate total heat gain through the window, the Average
solar gain factor env. property represents the average solar gain over a 24
hour period for the air inside the room (inside the internal shading). Solar
gain factor refers to an estimate of the heat gain due to transmitted and
absorbed solar energy through a benchmark glazing (1/8 or 3 mm clear glass) at
a specific latitude, time and orientation.
- Cyclic solar gain
factor env. light — Used to calculate total heat gain through the window, the
Cyclic solar gain factor env. light property represents the hourly swing of the
solar gain over a 24 hour period for the air inside the room (inside the
internal shading) for thermally light rooms. A thermally light room retains the
transmitted solar energy to a lesser degree from a thermally heavy room. Solar
gain factor refers to an estimate of the heat gain due to transmitted and
absorbed solar energy through a benchmark glazing (1/8 or 3 mm clear glass) at
a specific latitude, time and orientation.
- Cyclic solar gain
factor env. heavy — Used to calculate total heat gain through the window, the
Cyclic solar gain factor env. heavy property represents the hourly swing of the
solar gain over a 24 hour period for the air inside the room (inside the
internal shading) for thermally heavy rooms. A thermally heavy room retains the
transmitted solar energy longer from a thermally light room. Solar gain factor
refers to an estimate of the heat gain due to transmitted and absorbed solar
energy through a benchmark glazing (1/8 or 3 mm clear glass) at a specific
latitude, time and orientation.
- The
below glazing types are also set according to the current part:
- Plastic glazing
- Metal Framing
(curtain wall/storefront)
- Metal Framing
(entrance door)
- Metal Framing
(all others), and
- Operable
|
| Additional options
|
Contains controls for identifying a construction
has special considerations affecting its thermal properties. Also, when the
selected construction is a window, contains controls used to manipulate glazing
data such as solar heat gains, gains coefficients and transmittance properties
for Window constructions.
- Pre-fabricated
metal construction — When on, the construction is considered to be a
pre-fabricated metal construction, and a correction is made to account for the
metal included in the construction.
- Steel-framed/joist
construction — When on, the construction is considered to have a steel
structure, and a correction is made to calculate the infiltration of thermal
energy through the steel structural in the construction.
- Heated construction
— When on, the construction is considered to have its own heat source, and a
correction is made to account for the heat in the construction.
- Swinging door —
When on, the construction is considered to be a swinging door, and a correction
is made to account for large temperature variations that can occur when the
door swings open.
|